31 WHEELED ROBOTS AND LUNAR CARS
Roburoc 6x6 wheeled articulated robot of Robosoft, Bidart, France dates from 2006. Payload 100 kg, speed 13 km/h, 3 Li-Ion battery pack, vertical wall : 25 cm, mass 160 kg, max slope 45°, skid steering. http://www.robosoft.com/eng/sous_categorie.php?id=1027 |
 |
Roburoc 6x6, http://www.nanoblog.com/past/2006/06/roburoc_6.htm
|
 |
Roburoc from ISIR, 2010, in Island with Ushuaia Team. http://guliverdesign.com/actu.html |
 |
Roburoc 6 articulated 6x6. Pict J M M at Villepinte, 2008 06. |
 |
Cutlass from Remotec http://www.jedsite.info/robots-charlie/charlie/cutlass_series/cutlass_series.html |
|
|
Mini indoor security robot from ECA, La Garde, France : INBOT, 2,1 kg, launch able. Many robots are manufactured by this brand. Note simplified transmissions to wheels used also with tracks. http://defense-update.com/products/m/miniROC.htm http://www.eca-robotics.com/index-fr.htm |
M6 articulated mobile robot of Robovolc project of Università degli, Studi di Catania, Sicilia, in early 2000, used to explore volcanic environment. http://www.robovolc.dees.unict.it/gallery/20010920%20-%20M6%20Etna.htm |
WorkPartner Robot. From University of Helsinki. See Chapter : 'Self-levelling vehicles'. http://autsys.tkk.fi/en/WorkPartner/Media |
Omnidirectional robots T1, T2, T3 of Utah State University in 1998-1999. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pbUSbyOfL6s |
|
Praetor Robot of Oto Melara. A little robot in the front can leave the Praetor.Picture J M M in 2008 at Villepinte. |
Wheeled robots of the 2000. Pictures J M M at Villepinte except low center (iRobot-LE, 1995). http://www.otomelara.it/OtoMelara/EN/Corporate/Product_and_Services/Robotics/Wheeled/index.sdo
|
 |
Intervention robots. Pict J M M at Villepinte 2004 06. |
 |
Robocup 2004 at Lisbon, Kohga and Outdor Edition. http://www.faculty.jacobs-university.de/anuechter/robots.html |
Robotic Mule 6x6 REX unveiled in 2009. It can carry 200 kg, Built by IAI, Israel. http://www.stratpost.com/israel-shows-off-robotic-mule |
Quattroped robot, 2011, of National Taiwan University fitted with wheels or legs for uneven terrains. It looks like RHex of Boston Dynamics. http://www.robotspacebrain.com/robot/the-quattroped/National-taiwan-university-develops-a-leg-wheel-hybrid-mobila.mp4 from : http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=a9N6Zb_K2Z0
|
PAWL-40 robot, 2007, of Collineo, Boucherville, Québec. Mobility system is inspired by Shrimp of EPFL, Lausanne. http://www.collineo.net/ |
|
Toolkit surveillance robot of Collineo, Wheeled-legged robots with legs, which can bend, for better mobility. |
Mini-Whegs robot with adhesive feet on vertical surface. University of Cleveland, Ohio. http://biorobots.cwru.edu/projects/climbing/ |
Mini-Whegs robot can run fast over uneven terrains and over obstacles taller than their body length. Case Western Univ, Cleveland, Ohio.http://biorobots.cwru.edu/projects/whegs/miniwhegs.html |
Whegs II Ultrasonic of Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, can detect too large obstacles to avoid them. The whegs can easily cross over others obstacles.http://biorobots.cwru.edu/projects/whegs/whegs.html |
Journey jBot 6x6 robot of 2005-2008 fitted with coil springs suspension and built by David Anderson Texas in his garage. http://www.geology.smu.edu/dpa-www/robo/jbot/index.html |
Wheeler 6x6 robot of 2008, from Granosik et al. and Technical University of Lodz, Poland. Equipped with passive joint as Genbu robot of S. Hirose. http://www.expo21xx.com/automation21xx/18935_st2_university/default.htm |
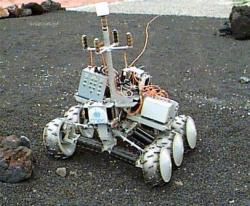
iRobot LE, 1995, was the was the first multipurpose domestic robot of iRobot Corporation, controlled through the Web and cameras. Front wheels on articulated arm helped to climb stairs. http://www.irobot.com/filelibrary/ppt/corp/cool_stuff_ppt/img13.html |
 |
iRobot LE |
GOAT (Goes Over All Terrain) UGCV robot, 2003, 4x4 robot of Cargenie Mellon University and Georgia Tech. Actuated arms allows to cross obstacles and to remain horizontal. http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~trb/goat/ |
Loper robot, 2008, from University of Minnesota, uses Tri-Star Wheels. http://www.tcdailyplanet.net/news/2011/12/22/department-defense-projects-bring-military-touch-civilian-research http://distrob.cs.umn.edu/loper.php |
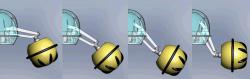
Epi.q robot. The arms of the Tri-Star wheel can be unfolded for crossing larger obstacles. http://www.dimec.unige.it/pmar/pages/research/robot/mobile%20robot/epiqrobot.htm |
|
This Epi.q robot also studied by University of Genova has no foldable legs but 4 Tri-Star wheels.http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6CMQfrJhHNw&feature=relatedhttp://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EuHxauea4LM |
|
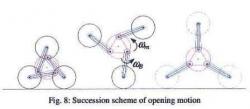
Epi.q-1 surveillance robot of Pr. Joseph Quaglia from University of Torino, using a Tri-Star wheels whose legs can be folded or unfolded for large obstacles. Epicyclical transmission to the wheels by 2 degrees of freedom is simple, the whole set of wheels being driven automatically by an obstacle.http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5qA90v9w02o&feature=related |
CKbot robot of University of Pennsylvania is a chain style modular robot small and inexpensive, manually reconfigurable for research on dynamic locomotion. http://www.ros.org/news/2010/04/robots-using-ros-modlabs-ckbots.html |
Asguard I and II, 2008, and Ceasar Robots of University of Bremen are 'whegs' robots. They were tested on a particularly well designed special track of the Robotic Center and Ceasar (below), the last of the family won 2009 ESA contest. http://robotik.dfki-bremen.de/en/research/robotsystems/asguard-i.html
|
|
Ceasar Lunar Robot, 2008. http://robotik.dfki-bremen.de/en/research/robotsystems/cesar.html |
ANT articulated 6x6 Robot Project of RDDC Suffield, Alberta, in early 2000 as demonstrator to evaluate outdoor mobile robots, fitted with wheels and legs for top locomotion. Unmanned and autonomous. http://www.drdc-rddc.gc.ca/drdc/fr/sciences/prog/ |






 R
R















































































































 Français
Français
 English
English
 Español
Español
 Italiano
Italiano
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 Nederlands
Nederlands
 Portuguesa
Portuguesa