|
|
|
|

|
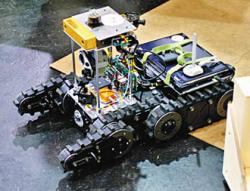
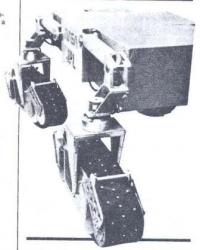
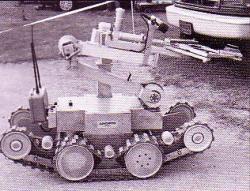
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Robot 85 cm long 35 cm wide, mass 6,3 kg. It is composed of 4 articulated lines with 18 wheels each of 4 cm diameter. Designed for moving in atomic power station, 2000. Pict from Sciences et Vie, April 2000.
|
|

|
Makro snake robot, 2000, from Fraunhofer Institute for Autonomous Intelligent Systems, St. Augustin, Germany. Makroplus, nowadays, is autonomous and is able to overcome obstacles. http://www.inspector-systems.com/makro_plus.html
|
|

|
Gavin Miller's snake like robots from the 90s to 2005 could crawl on flat soils and were very realistic. Passive wheels assist movement.
lehre/2009ws/seminar/
ir/PDF/snake-like%20robot.pdf
|
|

|
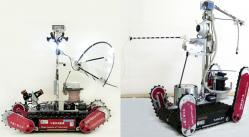
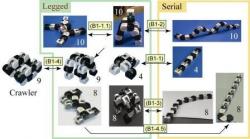
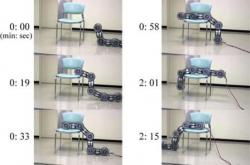
Carnegie Mellon snake-like robot, 2010. This new snake-like robot can move forward on relatively flat ground by waves, roll, sideways and wrap around a tree trunk or inside a pipe. Others snakes bots exists like Anna Konda, HiBot Amphibious snake, Unified Snake robot of CMU Biorobotics Lab, Gavin Miller Bots, Sand Snake Robots of Georgia Institute of Technology, Snake Robot of St Petersburg and others. http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~biorobotics/serpentine/serpentine.html
|
|

|
ACM-R5 Amphibious robot realized by Shigeo Hirose, Tokyo. It was the first to build snake-like robots. This robot moves forward on ground and water by lateral undulating and wheels are not driven. It seems today (May 2011) that snake-like robots propelled by waves cannot progress on uneven grounds like true snakes. This means they need sensors or additional tracks, wheels or legs to move without undulating.
|
|

|
Omniped Snake robot propelled by legs (and not waves) of University of Michigan in 2002-2003.
|
|

|
Polybot snakebot, in 2002 of Xerox Palo Alto Research Center, CA and NASA's Ames Research Center, Moffetts, CA. This rather old model was said to be able to go over obstacles (there are no videos) in the future and it seems it needed more sensors to progress much better on rocky grounds. It could move inchworm, flip over, coil and side-wind. http://stuff.dewsoft
overseas.com/snakebot.htm
|
|

|
Polybot snake robot G3 in early 2000, from NASA and PARC could be configured into loop to climb upstairs or in line using vertical undulations (sinusoidal waves) to go forwards or downstairs. First generation, in the 90s, were Polybots and Polypod of PARC, Stanford, which were reconfigurable in snake, legged spider, rolling track, earthworm. It does not seem that really off-road snake-robots moving by lateral undulations exists nowadays. http://spectrum.ieee.org/robotics/industrial-robots/modular-robots/0 http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/in_depth/sci_tech/2001/san_francisco/1173559.stm
|
|

|
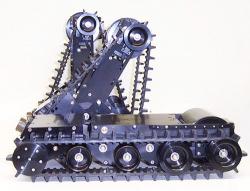
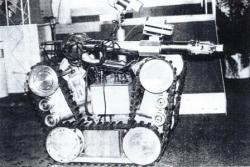
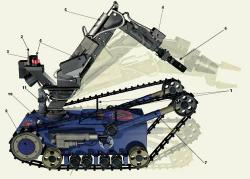
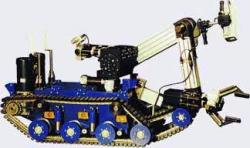
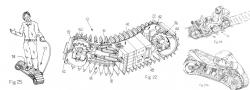
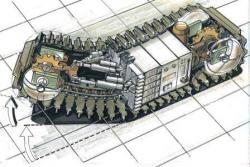
Millibot train semi-autonomous articulated tracked robot was built in 2002 at Carnegie Mellon University. The Millibot Train concept provided couplers that allowed the Millibot modules to engage/disengage under computer control and joint actuators that allowed lifting of one module by another and control the whole train shape in two dimensions. http://www.cs.cmu.edu/
~hbb/
|












 T
T

































































































































































 Français
Français
 English
English
 Español
Español
 Italiano
Italiano
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 Nederlands
Nederlands
 Portuguesa
Portuguesa