SELF-LEVELING VEHICLES
SELF-LEVELING VEHICLES
A self-leveling vehicle is an all-terrain vehicle that remains horizontal regardless of the slope, like a 'Dahu'. According to legend, the Dahu, mountain animal kind of goat or chamois, had the legs to the right different length from the left and thus walking up vertical mountainside.
Almost all these vehicles have a hydraulic system, often with an electronic servo controlled by a pendulum. Of course, this complication allows vehicles thus designed to vary the tilt of the machine to prevent tipping, to some extent. Variable ground clearance is an advantage over soft, wet ground or to go over obstacles. Similarly, the track between the wheels, sometimes variable, allows for greater stability on slopes.
1 - VEHICLES
1.1 - WHEELED VEHICLES
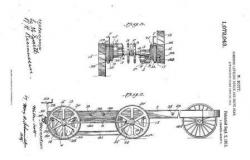
1 - Self-leveling vehicles patents existed since the beginnings of mechanical locomotion. That of W. Scott filed in 1913 attests. US1072043 patent
|
|
2 - However, combine harvesters, although not truly all terrain, were the first practical applications in this field. The Holt Company, California, conceived in 1891 a machine to harvest the slopes of the Palouse region of North-Eastern of USA. This avoids disturbing the threshing mechanism and reversal. Mercury button, invented by Raymond Hanson, appeared in 1946, had a switch to control the systems of horizontalityof the machine.The Case International harvester 453 (photo), made from 1970 to 1978, was maintained in the horizontal direction of the width but also length. Nowadays, all brands of combine harvesters offer such models. |
|
3 - It seems that the first all-terrain vehicle running horizontally on hillsides was the METRAC of Meili AG, Shaffhausen, in 1958, thanks to its hydraulic system. See chapter : 'The Meili Tractors and Gama Goat'. It will be created on that model the Kassbohrer Flexmobil in 1960 and Clark Flex-Trac in 1961. http://www.vmeili.ch/main/p_id/435/obj/67/nav/435/nav2/435/lang/7.html
|
|
4 - The Wagner brothers of 'Wagner Tractors' in 1961 revealed an amphibious prototype which will tour the world, at least in magazines : the Go-Devil or Do-Liner whose wheel arms fully orbited 360 degrees around their axis and .allowed the vehicle to cross high barriers and to swim thanks to manual controls in the cab. See chapter : 'The Go-Devil of Wagner'. Pict J M M collection.
|
|
5 - Roe Canada Ltd., Malton, Ontario in 1961, became Hawker-Siddeley Canada Ltd., Toronto, Ontario, created Gemini, an articulated 4x4 prototype with an air cushion that would help the wheels in soft terrains such as Muskeg in Northern Canada. An early prototype was built without joint to try the concept but the most difficult was the development of a flexible and hollow joint for the passage of air between the two bodies. This vehicle, suspended by arms and hydraulic cylinders could be able to roll horizontally regardless of the field. Gas turbine of 250 horsepower, payload 1 T for 2.25 T empty, maximum ground clearance 60 cm. McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario, became involved in the project. View Chapter : More Documentation, Articulated 4x4 Vehicles, Medium'. Pict from Jet Magazine, N°3, Jan 1962.
|
|
6 - Pekazett Company, Zweibrücken, Germany, founded in 1884 by Carl Peschke manufactured mixers. In the 60s, a three-wheeled tractor with rear axle controlled by a hydraulic system controlled itself by a pendulum allowed it to move horizontally on the slopes without roll over. Indeed, a survey of the period 1962 and 1963 in Germany revealed that 70% of serious accidents were caused by overturning of tractors. Fifteen of these tractors were built and employed in felling trees in the Palatinate Forest.This company later manufactured under license Menzi Muck walking excavators and tower cranes for the building. In 1974, the original company went bankrupt, but three former employees continued their work until its takeover by MAN. Today, the company still manufactures tower cranes.Pict of Journal of Terramechanics, 1970, Vol 7, N°1, Pergamon Press, later Elsevier. |
|
|
|
7 - The Pekazett tractor rear view. |
8 - The X-Musen, Swedish wheeled articulated test vehicle about 1965, looked like the Go-Devil Wagner with wheels able of full orbiting 360 °. Pict J M M collection (from Fordon Museum, Malmköping, Sweden, now at Arsenalen Museum, Strängnas).
|
|
9 - Exhibit of X-Musen in August 1987 at Fordon Museum. Pict from 'Wheels and Tracks' N° 23.
|
|
10 - This prototype was exposed to the Militär Fordon Historik Föreningen Museum, Malmköping, before 2009. It is now at the Arsenalen Museum, Strängnas, Sweden |
11 - The same vehicle in April 2010 at Strägnas is in perfect condition. It will be on display at the extension of the new Museum of Strängnas, Sweden, in 2013. See chapter : 'More Documentation' : 'Self-Levelling Vehicles'. |
|
12 - The prototype of James Bird, Tulsa, Oklahoma, appeared in 'Popular Science' in January 1971. Six wheels, each mounted on a double arm could rise and fall of almost 2 m. The main gasoline motor was operating the hydraulic motors in the 6 wheels. |
|
13 - The CVT in 1985 by Standard Manufacturing Co, Dallas, Texas, who introduced the 8x8 vehicles with hydrostatic transmission and innovative suspension, the TAD, Trailing Arm Drive, was also a 'Dahu'. The non-steered wheels imposed skid steering. Several models were tested without a series production. STV (Standard Tactical Vehicle) 8x8 prototype of the same firm is now parked (outside) at WES, Waterways Experiment Station, Vicksburg, Mississippi. Pict J M M collection.
|
|
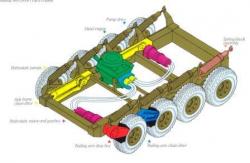
14 - We can see the frame, the arms (TAD) and hydrostatic transmission of the vehicles of Standard Manufacturing Co. |
|
|
|
15 - Another concept car, the Renault Racoon in 1993, off-road and amphibious intended to demonstrate the mastery of technology of Renault received a 3 liters twin turbo V6 engine for a speed of 155 km / h, 2 water jets, a variable high ground clearance, oversized tires, long arms suspension and a bubble. Cockpit gave a decidedly unusual appearance.http://www.carstyling.ru/en/car/1993_renault_racoon/images/697/ |
16 - The four side arms of the suspension of Racoon were actuated by hydraulic cylinders, which meant that horizontality was possible on the slopes but it seems that no picture (or video) thus represents it.http://www.carstyling.ru/en/car/1993_renault_racoon/images/700/ |
|
 |
17 - The Toyota Mogul, concept car seen at the 1995 at Tokyo Motor Show, remained horizontal. The inner wheels could be braked and the outer wheels accelerated to increase maneuverability in turns. Additional caterpillars could replace the wheels. Pict from review 'Passion 4x4', Jan 1996.
|
18 - Toyota Mogul in the longitudinal direction. Pict from review 'Passion 4x4', Jan 1996. |
|
19 - The Chainlink is a 4x4 whose wheels are driven by chains inside arms, built in 2003 in his garage by Cameron Carlson, an outstanding engineer. Weighing 2.5 T, too heavy to participate in rock crawling championships for which it was expected, each wheel is independently controlled from the driver’s cab by giving a displacement of 2 m between the front wheels and a little less rear : 1.5 m. The side wheel arms front and rear are connected by a double lever. It is possible to connect the wheels right and left or front and rear. A suspension with coil springs and air shocks completes the package. Ford V8 engine, Ford Bronco transmission, final reduction in each wheel 2:1, front-wheel steering and skid-steering, welded tubes body.http://jalopnik.com/cameron-carlson-chainlink/Very impressive, however, should computerize Chainlink to make its driving easier. Here are two videos:http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=w_F7QrR4Ur8http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=--zuMm0BlR8 |
|
20 - Chainlink 4x4 of Cameron Carlson |
21 - Chainlink 4x4 of Cameron Carlson |
|
22 - Chainlink of Cameron Carlson |
|
23 - Todd Gronsdahl, California, built this Toyota Land Cruiser FJ-40 Custom / Buggy Snow Cruiser with independent Gama Goat suspension front and rear controlled by compressed air cylinders that raise or lower the wheels with the help of a joystick inside the cockpit. Aluminum cabin, light platform, variable ground clearance and much power allow it theoretically running in snow without sinking. Seen in '4 Wheel & Off-Road’ in March 2008. |
1.2 - TRACKED VEHICLES
|
|
24 - William H. 'Bill' Schomers, who created Kristi Company, built his first tracked snow-cat, the 'Bear-Cat', in 1955 with a patented system of parallelograms sustaining the machine in the horizontal width direction. In all seven were built. Pict from : http://www.google.com/patents?id=O25sAAAAEBAJ&pg=PA2&dq=2967578&source=gbs_selected_pages&cad=2#v=onepage&q=2967578&f=falseSee also the site :http://www.kristisnowcat.com/history/index.asp
|
|
|
25 - In 1957, Kristi Company, Arvada, and later Broomfield, Colorado, was created. Subsequently, all the tracked vehicles of the brand : KT-2, KT-3 (photo), KT-4, KT-7 could roll hillsides up to 25 ° horizontally thanks to two hydraulic arms per track.180 snow cats of Kristi Company were built between 1953 and 1968. All could run horizontally hillsides. At that time it was the only case of mass produced vehicles with this feature except some excavators from 1966 studied for a different use. Pict from : http://www.safetyoneinc.com/specsheets/kristi.kt3.1.htmlSee also the site :http://www.kristisnowcat.com/history/index.asp
|
See the site :http://www.kristisnowcat.com/history/prototypes/KT4JC/kt4jcgallery.asp |
26 - Water Walker KT-4 JC Kristi prototype for U.S. Army, on the basis of a KT-4, in 1962, had tracks being provided fitted with floats (See chapter 'Pneumatic Tracks'). Shown here without the floats, a hydraulic system allowed level in the longitudinal direction only by means of levers and cylinders. |
See the site :http://www.kristisnowcat.com/history/prototypes/KT4JC/kt4jcgallery.asp |
27 - Kriti SnowCat KT4 JCInformation text of pictures 26-27 comes from site : http://www.kristisnowcat.com/ |
28 - In 1968, the tracked great spreader for slopes of Swanson's Spray and Manufacturing Inc. of Palouse, Washington, was more than 7 m long, 50 meter wingspan for a total mass of 18 T. http://www.exactrix.com/LargestApp.htm
|
|
29 - The Camoscio tractor, cover of magazine 'Off-Road' in November 1978, offered a very impressive front deflection of the tracks. However, the likely absence of hydraulic cylinders or other means make doubt his ability to remain level. |
2 - ROBOTS
2.1 - WHEELED ROBOTS
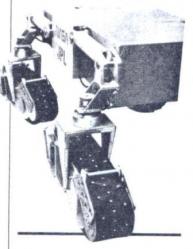
30 - The Russian Mars rover in 1978 EOSAIII-1 named ’Wheel-Walker’ with a mass of 480 kg, had six wheels that could be automatically lifted on one side and lowered on the otherto prevent sliding on the crumbly slopes until 30-32 °. Speed, very low, 0.3 km / h in stock mode and 0.02 km / h walking mode. |
|
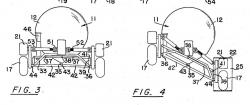
31 – 32 - They can see the system of arms embedded to wheels for this Mars rover. |
|
|
|
|
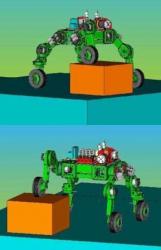
33 - Work Partner is an articulated robot developed by the University of Helsinki, Finland, together with the Rover Company Ltd, St Petersburg, Russia, for mechanical parts, revealed in March 2004. It is equipped with a manipulator of human form in its final version. Gasoline engine and batteries make it a hybrid robot with a maximum speed of 7 km / h for a mass of 230 kg. Fitted with 4 electric articulated legs and wheels, it can run and walk (rolking) thanks to his legs and can remain always horizontal, like most walking robots. |
|
34 - The Scarab Lunar Robot of Carnegie Mellon University and NASA in 2007, weighing 400 kg, was designed to carry a drill to find water in holes 1 m deep. It is therefore expected to land on the ground and stay horizontal on slopes with a suspension system of levers and cylinders. The wheels in this picture are the Michelin Tweel able to operate at extreme temperatures in the low gravity, not to slip on slopes and to resist lateral forces caused by the shifting direction.http://www.frc.ri.cmu.edu/project/lri/scarab/index.html |
|
35 - The robot Athlete in 2009 revealed for the second generation was a robot with six articulated legs and wheels to absorb any slopes of 35 °. Designed by Brian Wilcox and engineers at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, JPL of NASA, Pasadena, Calif., this was a giant robot : 7.5 m wide and legs 6 m long, planned to raise up to 6 m high and transport in all-terrain habitation modules for astronauts.If the wheels were to get stuck, it switches to 'walking' mode. Other modules such as grabs, drills or else were interchangeable. One arm can be used alone to lift or handle a load. It is expected to do large distances on the moon at 10 km / h maximum.http://www.robotics.jpl.nasa.gov/systems/systemImage.cfm?System=11&Image=393 |
|
36 - Collineo, Drummondville, Quebec, built with DRDC Suffield, for rescue or surveillance missions, the very sophisticated Micro-Hydraulic Toolkit robot, with wheels at the end of articulated arms in two parts.http://cradpdf.drdc-rddc.gc.ca/PDFS/unc95/p530428_A1b.pdf
|
|
37 - The Hylos II robot about 2006-2007 of ISIR, Institute of Intelligent Systems and Robotics, Pierre and Marie Curie University, Paris, produced this articulated legged and wheeled robot. The peristaltic operating mode allows forwarding especially in the sandy slopes.http://guliverdesign.com/hylos.html |
|
38 - It may be mentioned robot Robotex, around 2009, with wheeled gear fitted with controlled and extendable arms which the video is very impressive : http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fXWBQkkor68It is in fact a fiction. |
2.2 - WALKING ROBOTS
Note that walking robots (e.g. 6 legs) whose a few hundreds (or thousands) prototypes were built, should all have by nature this characteristic of horizontality, precisely through their legs. It is difficult to find images thus representing them.
2.3 - ROBOT ELMS
3 - FOREST MACHINES
3.1 - WHEELED MACHINES
44 - Log Max AB, 20 years of experience in forestry work, acquired Eco-Log Söderhamm, Sweden, and the product line of the same name to Caterpillar in 2004. 4x4 or 6x6 harvesters are designed to work in mountain forests and as such are equipped with suspension arms actuated by cylinders.http://www.eco-log.se/en/products/560D |
|
45 - The 5000 Rottne harvester competes Eco-Log harvesters. This one dates from 1998. |
|
46 - The Highlander of Konrad Company, Austria, forest gear for inclined plots and unveiled in 2005, fits a 250 hp engine, weighing 20 tons, 4 drive and steering wheels can be individually operated by rotating telescopic arm. The track can go from 4.8 to 6.8 m. Maximum slope is 35% and turning radius of only 4 meters.http://www.forsttechnik.at/highlander-mobility/ |
|
47 - The walking excavators whose first date of 1966, such Menzi-Muck, Kaiser (picture, Kaiser SX) or Euromach are particularly suited to slopes for earthworks or forestry. |
|
48 - The 'small' radio controlled RCM Harvester of OY RCM Harvester Ltd in Kangasala, Finland, a subsidiary of the Artekno Ltd Company , Kangra, Finland, very elaborate forest product contains a hydraulic system that powers the hydraulic motors of 4 wheels and outriggers connected to an onboard computer together with boom and harvester heads. Deutz Engine 47.5 kW.http://www.rcmharvester.fi/index.php?PAGE=2&NODE_ID=2&LANG=1 |
|
49 - RCM Harvesterhttp://www.rcmharvester.fi/index.php?PAGE=2&NODE_ID=2&LANG=1 |
|
50 - The cut trunks can be loaded onto the rear deck.http://www.rcmharvester.fi/index.php?PAGE=2&NODE_ID=2&LANG=1 |
|
51 - The Lucane BB TECH, Monceau les Mines, France, invented and produced by Hervé Charrière and unveiled in 2007 is an automatic system for cutting, splitting and conditioning the logs of heating, on site, in the forest and requiring a single operator. Engine 100 hp, Poclain transmission to 8 driven wheels, whose the four first are steered and leveling of 30% in both axes. Reduced impact on the ground (mass 9 T).Another example is the t-bucket Mecaplus ME12 SL used in arboriculture. http://www.bioenergie-promotion.fr/557/bbtech-automoteur-pour-produire-des-buches-en-foret/Company in liquidation since June 2011.
|
3.2 – TRACKED MACHINES
52 - ATH 28, Allied Tree Havester of Allied System Company, Sherwood, Oregon, manufactured since the 90s this 4 independent tracks and hydrostatic transmission harvester of 210 hp with stabilizing system in slopes up to 70%. Maximum speed 1.9 km / h.http://www.alliedsystems.com/ath/ath.htm |
|
53 - The TTM, Tri-Trac-Mover, a prototype of the Forest Institute of Forest Products of Japan in 1997 consisted of three groups of two tracks linked together by a parallelogram controlled armature. Each group had its diesel engine and hydraulic transmission. This system allowed it to climb over an obstacle up to 1.3 m and move on slopes of 28 ° strewn with pitfalls.http://www.ffpri.affrc.go.jp/labs/zoki/ttm/ttm-j1.html |
|
54 - The Timbco Company, became Valmet then Komatsu, Tokyo, Japan, marketed in 1997 the Haverter 425 B with 260 hp Cummings engine. Here, the cab was moving vertically. |
|
55 - Today, all manufacturers of forest harvesters (e.g.: John Deere, Wacker Neuson-, Tangay and many others) offer similar pattern, the tilt cab, as also this Impex Fortsmaschinen GMBH, Langquaid, Germany, which manufactures several harvester models, especially this Königstiger T 30 (picture).http://www.impex-forstmaschinen.de/gallery.htm |
|
56 - The Safe Trak GreenMech Ltd, Alcester, Warwickshire, England, is a wood chipper with a patented device to track allowing a large ground clearance (up to 600 mm) with incoming and outgoing legs can absorb 35 ° slope safely despite a loaded machine. The reversal occurs only at an angle of 60 °.The Multitask MT120 trimmer and the shredder Quad Trac of the same company are fitted with the same attachment device of caterpillars.http://www.greenmech.co.uk/safe-trak-16-23/ |
|
57 - The tracked wood chipper Timberwolf TW190TVGTR of Environmental Manufacturing LLP, Stowmarket, Suffolk, founded in 1986, presents the Wolftrack new system having controlled arms supporting each track and allowing to varying the ground clearance, tracking (2 m max) and inclination of the machine. Kubota 45 HP engine, 1740 kg.http://www.timberwolf-uk.com/Templates/190tvgtrinfopg.html |
|
58 - View of the tilt mechanism Wolftrack.http://www.timberwolf-uk.com/Templates/190tvgtrinfopg.html |
4 - THE MACHINE THAT WALKS
59 - Plustech Oy, Tampere, Finland, Timberjack Research Centre introduced this prototype of walking forestry machine concept, whose could see the first prototype in 1995 after 4 years of research. This technology is very suited to slopes and crossing of rocks through its software and sensors.http://www.hexapodrobot.com/forum/viewtopic.php?f=13&t=171 |
|
60 and 61 - Plustech, seen here in 2002, had several awards for innovation and environment. The operator can adjust the ground clearance, the height of steps and all controls of the saw head by a single joystick. Timberjack no longer exists and Plustech Oy was sold to John Deere in 2006.http://www.majhost.com/cgi-bin/gallery.cgi?f=161102 |
|
61 - Plustechhttp://www.majhost.com/cgi-bin/gallery.cgi?f=161102 |

























































 Français
Français
 English
English
 Español
Español
 Italiano
Italiano
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 Nederlands
Nederlands
 Portuguesa
Portuguesa